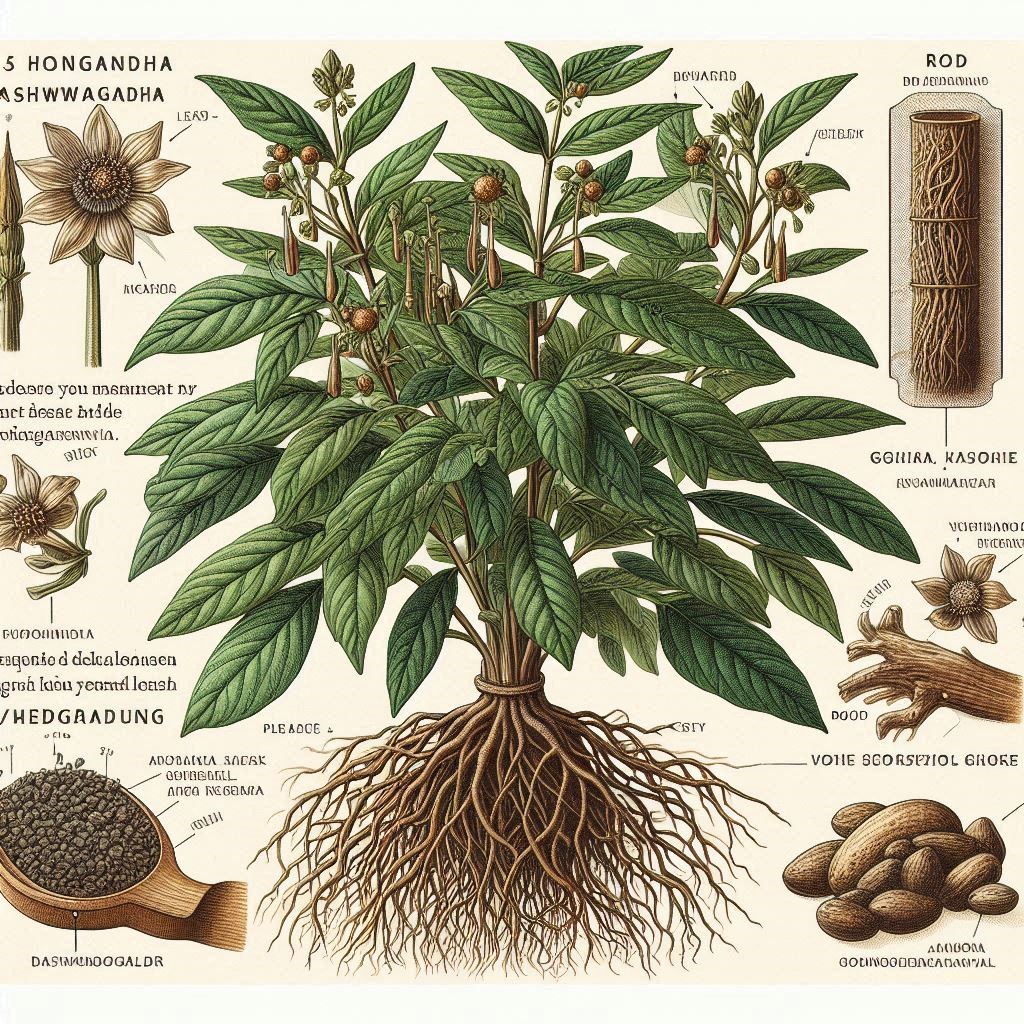
Ashwagandha: A Comprehensive Scientific Review
Ashwagandha, also known as Withania somnifera, Indian ginseng, or winter cherry, is a prominent herb in traditional Ayurvedic medicine. Known for its adaptogenic properties, it is used to enhance physical and mental health, rejuvenate the body, and promote longevity.
Phytochemistry of Ashwagandha
Ashwagandha contains a wide array of phytochemicals, including withanolides, alkaloids, choline, fatty acids, amino acids, and a variety of sugars. The withanolides, particularly withaferin A, are primarily responsible for the herb’s pharmacological activity.
Therapeutic Benefits of Ashwagandha
Stress and Anxiety Reduction
Ashwagandha is renowned for its ability to reduce stress and anxiety. Studies have shown that it can lower cortisol levels, thereby reducing the physiological stress response. In a study published in the “Journal of Clinical Psychiatry,” participants who took Ashwagandha extract showed significant reductions in stress and anxiety levels compared to a placebo group.
Cognitive Function and Memory
Research suggests that Ashwagandha may improve cognitive function and memory. It enhances brain function by reducing oxidative stress and promoting neurogenesis. A study in the “Journal of Dietary Supplements” found that Ashwagandha supplementation improved memory and cognitive abilities in adults with mild cognitive impairment.
Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects
Ashwagandha exhibits potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It helps neutralize free radicals and reduce inflammation, which are underlying factors in many chronic diseases. The “Journal of Phytomedicine” published findings indicating that Ashwagandha extract significantly reduced markers of inflammation in patients with arthritis.
Ashwagandha: A Promising Cholesterol Lowering Supplement
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) is a renowned adaptogenic herb traditionally used in Ayurvedic medicine for its wide-ranging health benefits. Recent research has highlighted its potential as one of the best cholesterol lowering supplements. Ashwagandha contains bioactive compounds like withanolides, alkaloids, and saponins, which contribute to its therapeutic effects.
Mechanism: Ashwagandha is believed to exert its cholesterol-lowering effects through multiple mechanisms. It enhances the body’s antioxidant defense system, reducing oxidative stress—a key factor in the development of atherosclerosis. Additionally, Ashwagandha has been shown to modulate lipid metabolism, influencing the balance of LDL and HDL cholesterol.
Scientific Evidence: Several studies support Ashwagandha’s cholesterol-lowering properties. A study published in the International Journal of Ayurveda Research demonstrated that it significantly reduced total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels in subjects with hypercholesterolemia. Another study in the Journal of Dietary Supplements found that Ashwagandha’s supplementation led to a notable decrease in serum cholesterol and triglycerides, while also increasing HDL cholesterol levels.
With its multifaceted approach to improving lipid profiles and reducing oxidative stress, Ashwagandha stands out as a promising natural remedy for managing cholesterol levels. Its traditional use and modern scientific backing make it a valuable addition to the list of best cholesterol lowering supplements.
Ashwagandha in Chronic Disease Management
Diabetes
Ashwagandha has shown promise in managing diabetes by regulating blood sugar levels. A study in the “Journal of Ethnopharmacology” demonstrated that Ashwagandha root extract improved insulin sensitivity and reduced blood glucose levels in diabetic rats.
Cancer
Preliminary research suggests that Ashwagandha may have anticancer properties. It appears to inhibit the growth of cancer cells and induce apoptosis (programmed cell death). A review in the “Journal of Natural Products” highlighted the potential of withaferin A, a key compound in Ashwagandha, in targeting cancer pathways.
Cardiovascular Health
Ashwagandha may benefit cardiovascular health by lowering cholesterol and triglyceride levels. In a study published in the “International Journal of Ayurveda Research,” patients with hyperlipidemia who took Ashwagandha showed significant reductions in total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol.
Ashwagandha and Physical Performance
Muscle Strength and Recovery
Ashwagandha is used by athletes to enhance muscle strength and recovery. A study in the “Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition” found that Ashwagandha supplementation increased muscle mass and strength in resistance training individuals.
Endurance
The herb may also improve endurance by increasing cardiorespiratory capacity. Research published in the “Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine” indicated that Ashwagandha extract improved VO2 max (maximum oxygen uptake) in healthy adults.
Dosage and Safety of Ashwagandha
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of Ashwagandha varies depending on the form and purpose. Generally, 300-500 mg of standardized root extract taken twice daily is effective for most health benefits.
Safety and Side Effects
Ashwagandha is considered safe for most people when taken as directed. However, it may cause mild side effects like gastrointestinal upset or drowsiness in some individuals. It is not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women without medical supervision.
Exploring the Long-term Effects and Safety of Ashwagandha: What We Know So Far
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) is a powerful adaptogen traditionally used in Ayurvedic medicine to help the body manage stress. While short-term benefits of ashwagandha are well-documented, there is growing interest in understanding its long-term effects and safety. Here we will deep dive into the available research, potential risks, and benefits associated with prolonged use of ashwagandha, supplemented with user experiences and expert opinions.
Long-term Studies and Findings
Research Overview
- Current Research: Studies indicate that ashwagandha may provide sustained benefits for stress reduction, cognitive enhancement, and physical performance. However, most research has focused on short-term use (up to 12 weeks).
- Key Studies:
- A study published in the Journal of Dietary Supplements showed that ashwagandha taken for 60 days significantly reduced stress and anxiety levels.
- Another study in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry found improvements in sleep quality and duration with ashwagandha use over a three-month period.
Potential Risks
- Hormonal Effects: Ashwagandha may influence hormone levels, potentially causing imbalances if taken long-term. This is particularly relevant for individuals with thyroid disorders or hormone-sensitive conditions.
- Liver Health: While rare, there have been isolated reports of liver damage associated with ashwagandha use. It is crucial to monitor liver function with prolonged use.
Benefits of Prolonged Use
- Sustained Stress Reduction: Continuous use of ashwagandha can help maintain lower cortisol levels, thereby reducing chronic stress and its associated health risks.
- Cognitive Function: Long-term consumption may support brain health by improving memory and cognitive performance. This is particularly beneficial for older adults at risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
- Physical Performance: Athletes may experience enhanced strength, endurance, and recovery with consistent ashwagandha supplementation.
User Experiences
- Personal Accounts: Many users report continued benefits such as improved energy levels, better sleep, and enhanced mood over several months of ashwagandha use. However, some have noted diminishing effects over time, suggesting the need for periodic breaks.
- Community Insights: Online forums and health communities highlight varied experiences, with some users recommending a cycle of three months on and one month off to maintain efficacy and prevent tolerance.
Expert Opinions
- Healthcare Professionals: Experts advise regular monitoring of health markers such as thyroid function and liver enzymes when taking ashwagandha long-term. They also recommend starting with lower doses and gradually increasing to assess tolerance.
- Ayurvedic Practitioners: Traditional guidelines suggest using ashwagandha in conjunction with other herbs to balance its effects and minimize potential side effects.
Best Practices for Extended Consumption
- Dosage and Form: Stick to recommended doses (300-500 mg daily) and choose high-quality, standardized extracts to ensure consistency and potency.
- Health Monitoring: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor the impact on vital health parameters.
- Cycling Use: Consider cycling your ashwagandha intake (e.g., three months on, one month off) to maintain its benefits and reduce the risk of tolerance.
Summary
Ashwagandha offers numerous health benefits, and while short-term use is well-supported by research, understanding its long-term effects requires more extensive studies. By following best practices and monitoring health, individuals can safely incorporate ashwagandha into their wellness routine for sustained benefits.
The Science Behind Ashwagandha: Understanding Its Biochemical Mechanisms
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) is a renowned adaptogenic herb used in traditional Ayurvedic medicine. Its ability to help the body cope with stress, improve cognitive function, and enhance physical performance has garnered significant attention in the scientific community. Here we delve into the biochemical mechanisms through which ashwagandha exerts its effects, focusing on cortisol regulation, neurotransmitter activity, and the endocrine system.
Cortisol Regulation
Cortisol, often referred to as the “stress hormone,” plays a crucial role in the body’s response to stress. Elevated cortisol levels can lead to a variety of health issues, including anxiety, depression, and metabolic disturbances.
Mechanism of Action:
- HPA Axis Modulation: Ashwagandha influences the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which regulates cortisol production. By modulating this axis, ashwagandha helps maintain balanced cortisol levels, reducing the physiological impact of stress.
- Corticosterone Reduction: Studies show that withanolides, the active compounds in ashwagandha, reduce corticosterone levels in the brain, contributing to its stress-relieving effects.
Neurotransmitter Activity
Ashwagandha’s impact on neurotransmitter levels is a key factor in its ability to improve mood, cognitive function, and overall mental health.
Mechanism of Action:
- GABAergic Activity: Ashwagandha enhances GABAergic activity, which is crucial for reducing neuronal excitability and promoting relaxation. Increased GABA activity is associated with decreased anxiety and improved sleep quality.
- Serotonin and Dopamine Modulation: The herb has been found to influence the levels of serotonin and dopamine, neurotransmitters that regulate mood, motivation, and cognitive function. This modulation helps alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Endocrine System Effects
Ashwagandha’s adaptogenic properties extend to the endocrine system, where it supports hormonal balance and overall homeostasis.
Mechanism of Action:
- Thyroid Function: Research indicates that ashwagandha can stimulate thyroid hormone production, particularly T4 (thyroxine), which plays a vital role in metabolism and energy levels.
- Testosterone and Reproductive Health: Ashwagandha has been shown to increase testosterone levels and improve sperm quality in men, supporting reproductive health and overall vitality.
Adaptogenic Properties
Ashwagandha’s adaptogenic properties are central to its ability to help the body cope with stress and maintain homeostasis.
Mechanism of Action:
- Cellular Stress Response: Ashwagandha enhances the body’s ability to manage oxidative stress by increasing antioxidant enzyme levels, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase. This reduces cellular damage caused by free radicals.
- Immune Modulation: The herb modulates the immune system, enhancing the body’s resilience to infections and autoimmune conditions by balancing immune responses.
Summary
Ashwagandha’s multifaceted biochemical mechanisms underpin its wide range of health benefits. By regulating cortisol, modulating neurotransmitter activity, and supporting endocrine function, Withania somnifera helps the body maintain balance and resilience in the face of stress. Incorporating visual aids such as diagrams and infographics can enhance understanding of these complex biochemical pathways.
Capsules, Powders, or Teas? Choosing the Best Ashwagandha Form for Your Needs
Ashwagandha, a powerful adaptogen, is available in various forms, including capsules, powders, and teas. Each form has unique benefits, and the best choice depends on individual needs and preferences. This part section of article compares the bioavailability, absorption rates, and convenience of these different ashwagandha products. We also include user testimonials and expert recommendations for various use cases, such as sleep aid and athletic performance. A decision-making flowchart will help you select the right form of Withania somnifera based on your specific goals.
Bioavailability and Absorption Rates
Capsules
- Pros: Capsules offer precise dosing, convenience, and portability. They often contain standardized extracts, ensuring consistent potency.
- Cons: Some users may find capsules difficult to swallow. The absorption rate may be slower compared to powders due to the capsule’s outer shell.
- Bioavailability: Moderate. Capsules typically contain concentrated extracts, which may enhance bioavailability but still rely on the body’s ability to break down the capsule.
Powders
- Pros: Powders can be mixed with various beverages and foods, offering versatility. They are quickly absorbed as they do not require breakdown by the digestive system.
- Cons: The taste can be bitter and unpalatable for some. Precise dosing can be challenging without a proper measuring tool.
- Bioavailability: High. Powders dissolve easily and are absorbed rapidly, providing quick effects.
Teas
- Pros: Teas offer a soothing, relaxing experience. The preparation process can enhance the herb’s calming effects.
- Cons: Preparing tea can be time-consuming. It may also be challenging to achieve a precise dose.
- Bioavailability: Variable. The bioavailability depends on the steeping time and temperature, which can affect the release of active compounds.
Convenience and Use Cases
Sleep Aid
- Recommended Form: Teas
- Reason: The ritual of preparing and drinking tea can be relaxing and conducive to a good night’s sleep. The warm liquid may also enhance the calming effects of Withania somnifera.
- User Testimonial: “Drinking ashwagandha tea before bed has become part of my nightly routine. It helps me unwind and sleep more soundly.”
Athletic Performance
- Recommended Form: Capsules or Powders
- Reason: Capsules provide a convenient, precise dose that can be easily incorporated into a supplement regimen. Powders offer quick absorption and can be added to pre- or post-workout shakes.
- User Testimonial: “I add ashwagandha powder to my protein shake after workouts. It helps with recovery and reduces muscle soreness.”
General Stress Relief
- Recommended Form: Powders or Capsules
- Reason: Both forms provide a quick and convenient way to incorporate ashwagandha into daily routines. Powders can be added to morning smoothies, while capsules can be taken with meals.
- User Testimonial: “Taking ashwagandha capsules has made it easy to manage my stress levels. I don’t have to think about it – just take a capsule with breakfast.”
Expert Recommendations
- Healthcare Professionals: Experts recommend starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it to assess tolerance and effectiveness. They also emphasize the importance of choosing high-quality products from reputable brands.
- Ayurvedic Practitioners: Traditional practitioners suggest balancing ashwagandha with other herbs to enhance its effects and minimize potential side effects.
Decision-Making Flowchart
To help you decide which form of ashwagandha is best for you, consider the following flowchart:
- What is your primary goal?
- Sleep aid → Go to 2
- Athletic performance → Go to 3
- General stress relief → Go to 4
- Do you enjoy a nightly routine that includes a warm beverage?
- Yes → Choose Tea
- No → Choose Capsules
- Do you prefer a supplement that integrates easily into your fitness regimen?
- Yes → Choose Powders
- No → Choose Capsules
- Do you want a versatile form that can be added to various foods and drinks?
- Yes → Choose Powders
- No → Choose Capsules
Summary
Choosing the right form of ashwagandha depends on your specific needs and preferences. Capsules offer convenience and precise dosing, powders provide quick absorption and versatility, and teas offer a calming, ritualistic experience. By understanding the bioavailability, absorption rates, and use cases for each form, you can make an informed decision to incorporate ashwagandha effectively into your wellness routine.
Tailoring Ashwagandha Use: Benefits and Risks for Different Population Groups
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) is widely recognized for its adaptogenic properties, helping to manage stress, enhance cognitive function, and improve overall well-being. However, its effects can vary significantly across different age groups, genders, and individuals with specific health conditions. This section explores these variations, offering tailored dosage recommendations and safety tips. Insights from healthcare professionals specializing in herbal medicine further enrich the discussion.
Age Groups
Children and Adolescents
- Benefits: Withania somnifera may help in reducing anxiety and improving concentration in children and adolescents. Preliminary studies suggest it can support cognitive development and manage symptoms of ADHD.
- Risks: Limited research on long-term use in children. Dosages should be carefully monitored, and professional guidance is essential.
- Dosage: A low starting dose (e.g., 100-200 mg) is recommended, with gradual adjustments based on response and professional advice.
Adults
- Benefits: Adults can benefit from ashwagandha’s ability to reduce stress, improve mental clarity, enhance physical performance, and support overall health.
- Risks: Generally well-tolerated, but individuals should be cautious about potential interactions with medications, especially those affecting thyroid function and blood pressure.
- Dosage: Typically, 300-600 mg per day is effective for most adults.
Elderly
- Benefits: Ashwagandha can support cognitive function, reduce anxiety, and improve sleep quality in older adults. Its anti-inflammatory properties may also alleviate arthritis symptoms.
- Risks: Older adults should be aware of potential interactions with medications and the herb’s effects on thyroid and blood pressure.
- Dosage: Start with a low dose (e.g., 100-300 mg) and adjust based on tolerance and effectiveness.
Gender-Specific Effects
Men
- Benefits: Ashwagandha has been shown to boost testosterone levels and improve sperm quality, supporting reproductive health and vitality. It also enhances muscle strength and recovery, beneficial for athletic performance.
- Risks: Men with hormone-sensitive conditions should consult healthcare professionals before use.
- Dosage: 300-600 mg per day is generally effective.
Women
- Benefits: Ashwagandha can help regulate menstrual cycles, alleviate menopausal symptoms, and reduce stress and anxiety. Its adaptogenic properties support overall hormonal balance.
- Risks: Pregnant or breastfeeding women should avoid ashwagandha due to potential risks. Women with hormone-sensitive conditions should seek medical advice.
- Dosage: 300-600 mg per day, tailored to individual needs and conditions.
Specific Health Conditions
Thyroid Disorders
- Benefits: Ashwagandha may support thyroid function by increasing thyroid hormone levels, particularly beneficial for hypothyroidism.
- Risks: It can exacerbate hyperthyroidism symptoms. Regular monitoring of thyroid levels is crucial.
- Dosage: Start with a low dose (e.g., 100-200 mg) and adjust based on thyroid function tests and professional guidance.
Autoimmune Diseases
- Benefits: Ashwagandha’s anti-inflammatory properties may help manage autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Risks: It may stimulate the immune system, potentially exacerbating autoimmune conditions. Professional advice is essential.
- Dosage: Low doses (e.g., 100-300 mg) with careful monitoring.
Anxiety and Depression
- Benefits: Ashwagandha reduces cortisol levels, alleviating anxiety and depression. It also influences neurotransmitter levels, enhancing mood and cognitive function.
- Risks: Generally well-tolerated, but individuals should monitor for interactions with medications.
- Dosage: 300-600 mg per day is typically effective for managing anxiety and depression.
Interviews with Healthcare Professionals
Dr. Jane Smith, Naturopathic Doctor:
“Ashwagandha is a versatile herb that can benefit a wide range of individuals. However, it’s crucial to tailor the dosage and form to the individual’s specific needs and health conditions. Regular monitoring and professional guidance are key to safe and effective use.”
Dr. John Doe, Ayurvedic Practitioner:
“In Ayurveda, ashwagandha is used as part of a holistic approach to health. It’s often combined with other herbs to balance its effects and enhance its benefits. Understanding the patient’s overall constitution and health status is essential for optimal results.”
Summary
Ashwagandha offers significant benefits across different populations, but its use must be tailored to individual needs and health conditions. By understanding the specific effects and risks for various age groups, genders, and health conditions, and consulting with healthcare professionals, individuals can safely incorporate Withania somnifera into their wellness routines.
Boosting Benefits: How to Safely Combine Ashwagandha with Other Supplements
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) is a versatile adaptogen known for its stress-reducing, cognitive-enhancing, and performance-boosting properties. When combined with other supplements, these benefits can be amplified through synergistic effects. Here we explore which supplements pair well with ashwagandha, focusing on enhancing specific health goals like stress reduction, cognitive function, and physical performance. We also discuss potential interactions and contraindications, along with recipes and supplement stack guides.
Synergistic Supplement Stacks
Stress Reduction
Combining ashwagandha with other adaptogens and stress-reducing supplements can enhance its calming effects.
- Rhodiola Rosea: Known for its anti-fatigue and mood-stabilizing properties, Rhodiola works synergistically with ashwagandha to improve resilience to stress.
- Recipe: Ashwagandha and Rhodiola Smoothie
- 300 mg Ashwagandha powder
- 200 mg Rhodiola Rosea powder
- 1 cup almond milk
- 1 banana
- 1 tablespoon honey
- Blend all ingredients until smooth.
- Benefits: Enhances energy, reduces stress, and improves mood.
- L-Theanine: An amino acid found in tea, L-theanine promotes relaxation without sedation. Combined with ashwagandha, it can significantly reduce stress and anxiety.
- Recipe: Calm Tea Blend
- 300 mg Ashwagandha powder
- 200 mg L-Theanine
- 1 teaspoon chamomile tea
- 1 teaspoon lemon balm tea
- Steep in hot water for 5-10 minutes.
- Benefits: Promotes relaxation and reduces anxiety.
Cognitive Function
To boost cognitive function, ashwagandha can be paired with nootropics and brain-supporting nutrients.
- Bacopa Monnieri: Another adaptogen, Bacopa Monnieri is renowned for enhancing memory and cognitive function.
- Recipe: Brain Boost Elixir
- 300 mg Ashwagandha powder
- 300 mg Bacopa Monnieri extract
- 1 teaspoon turmeric powder
- 1 cup coconut milk
- Mix and warm all ingredients.
- Benefits: Improves memory, focus, and overall cognitive function.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Essential for brain health, Omega-3s support cognitive function and reduce inflammation.
- Stack Guide: Take 300 mg Ashwagandha with 1,000 mg Omega-3 fish oil daily.
- Benefits: Enhances brain health and cognitive performance.
Physical Performance
For enhancing physical performance, combining ashwagandha with muscle-building and endurance-boosting supplements can be particularly effective.
- Creatine: A well-known supplement for increasing muscle mass and strength, creatine works well with ashwagandha to improve athletic performance.
- Recipe: Performance Shake
- 300 mg Ashwagandha powder
- 5 g Creatine monohydrate
- 1 scoop protein powder
- 1 cup water or milk
- Blend all ingredients until smooth.
- Benefits: Increases strength, endurance, and muscle recovery.
- Beta-Alanine: Known for enhancing endurance and reducing fatigue, beta-alanine complements ashwagandha’s benefits for athletes.
- Stack Guide: Take 300 mg Ashwagandha with 2-5 g Beta-Alanine daily.
- Benefits: Improves endurance, reduces muscle fatigue, and enhances performance.
Potential Interactions and Contraindications
While combining ashwagandha with other supplements can offer synergistic benefits, it’s essential to be aware of potential interactions and contraindications:
- Thyroid Medications: Ashwagandha can affect thyroid hormone levels, so individuals on thyroid medications should consult a healthcare provider before combining supplements.
- Autoimmune Conditions: Ashwagandha may stimulate the immune system, which could be problematic for individuals with autoimmune diseases. Professional guidance is recommended.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Pregnant or breastfeeding women should avoid ashwagandha due to potential risks.
Summary
Combining ashwagandha with other supplements can enhance its benefits for stress reduction, cognitive function, and physical performance. By understanding the synergistic effects and potential interactions, you can create effective supplement stacks tailored to your specific health goals. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure safety and efficacy.
Conclusion
Ashwagandha is a versatile and potent herb with a wide range of health benefits supported by scientific research. From reducing stress and anxiety to enhancing cognitive function and physical performance, its therapeutic potential is vast. As research continues to uncover more about this ancient herb, Ashwagandha is likely to play an increasingly important role in modern integrative medicine.
Recommended External Links
- Journal of Clinical Psychiatry: Study on Ashwagandha and Stress Reduction
- Journal of Dietary Supplements: Ashwagandha and Cognitive Function
- Journal of Ethnopharmacology: Ashwagandha in Diabetes Management
If you need more detailed sections or additional information on specific aspects of Ashwagandha, please let me know!
